The Next Frontier in Energy-Efficient Heating: Advanced Heat Pumps
How Cutting-Edge Heat Pump Innovations are Redefining the Future of Heating and Cooling
This article highlights the potential of advanced and energy-efficient heat pumps across the heating and cooling industry, which accounts for half of the global energy consumption and over 40% of CO2 emissions. Rising global temperatures are driving up the need for cooling, but many buildings are still dependent on fossil fuels.
Electricity-driven heat pumps offering high efficiency and low emissions, are becoming preferred solutions for space and water heating. These pumps can integrate with traditional systems, provide grid services, and generate revenue. The heat pump market, valued at USD 57.9 billion in 2023, is projected to grow at a 12.9% CAGR from 2024-2032, driven by greenhouse gas reduction efforts, clean energy measures, financial incentives, and their low carbon footprint.

Additionally, industrial and district heating systems stand to benefit significantly from these advancements. Industrial heat pumps can handle higher capacities and temperatures, making them ideal for large-scale operations. District heating systems, prevalent in urban areas, can cut down fossil fuel reliance and emissions, aligning with global sustainability goals.
Introduction
A heat pump consists of a compressor and heat exchangers to move and amplify heat from sources like air, ground, water, or industrial waste. This makes it more efficient and cost-effective than boilers or electric heaters. Heat pumps produce several times more heat than the electricity they use.
Heat pumps are 3-5 times more energy-efficient than natural gas boilers and reduce exposure to fossil fuel price spikes. They account for one-sixth of global natural gas demand for heating, one-third in the EU. They also provide cooling, potentially eliminating separate air conditioners for 2.6 billion people by 2050. Heating in buildings emits 4 gigatons of CO2 annually (10% of global emissions). Replacing fossil-fuel boilers with heat pumps can significantly reduce emissions, especially as electricity systems decarbonize[1].

Conventional Heat Pump Technology
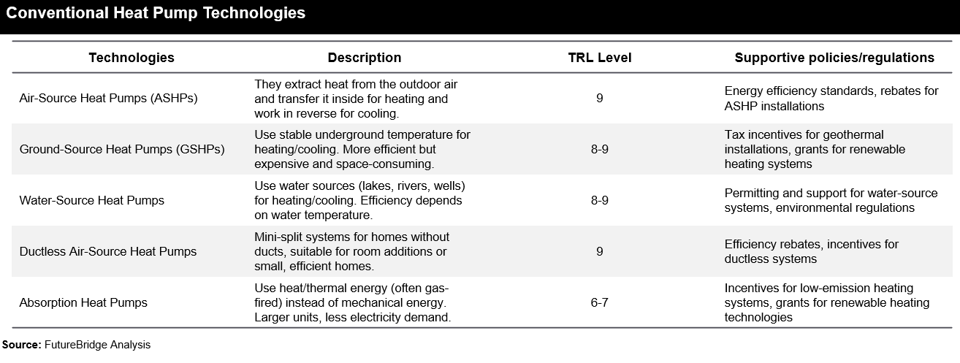
Three main types of compression heat pumps are driven by mechanical energy connected by ducts: air-to-air, water source, and geothermal. They collect heat from the air, water, or ground outside your home and concentrate it for use inside.

Next-Generation Heat Pump Technologies
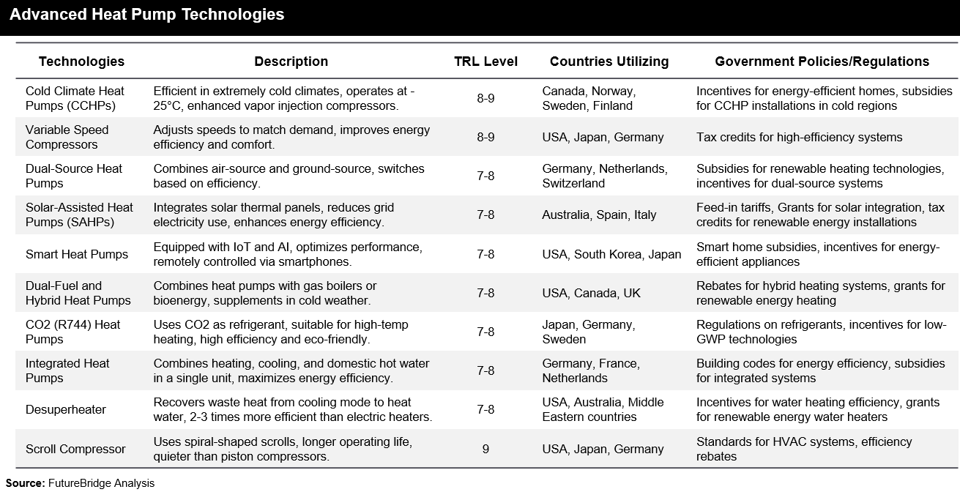
Advanced heat pump technologies aim to address the limitations of conventional systems, particularly in extreme weather conditions and energy efficiency. Key advancements include:

How heating needs are addressed in both Industry and district heating
-
The industrial sector
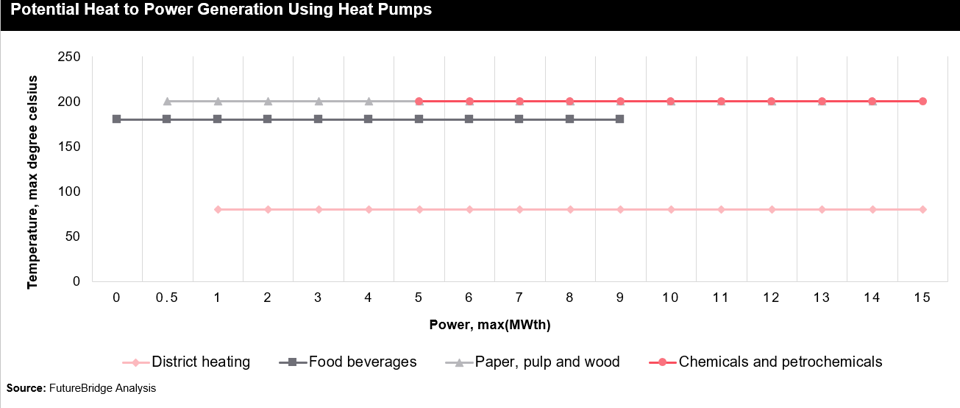
It is responsible for one-third of global CO2 emissions and must address its fossil-based heating, which accounts for over 85% of its energy use, primarily from natural gas, coal, and oil, compared to about 10% from biomass. Industrial heat pumps, using electricity and low-temperature sources like seawater and sewage, can efficiently supply heat, delivering 3-5 times more heat per unit of electricity than traditional heaters, and can reach up to 200ºC and beyond ten thermal megawatts. Despite their efficiency and economic benefits, heat pumps currently only provide 5% of global industrial heat.

Market growth and adoption
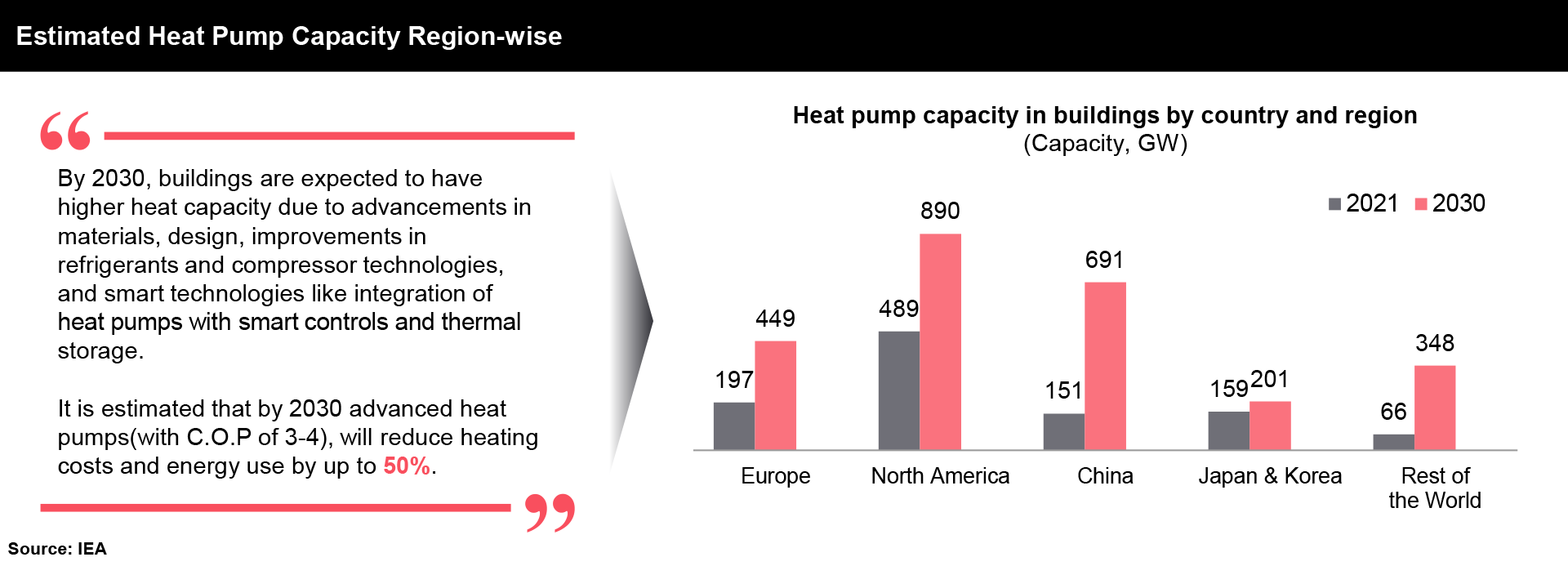
Global Capacity: The global capacity of heat pumps is projected to rise from 1,000 GW in 2021 to 2,600 GW by 2030. This increase is expected to significantly reduce reliance on fossil fuels for heating.
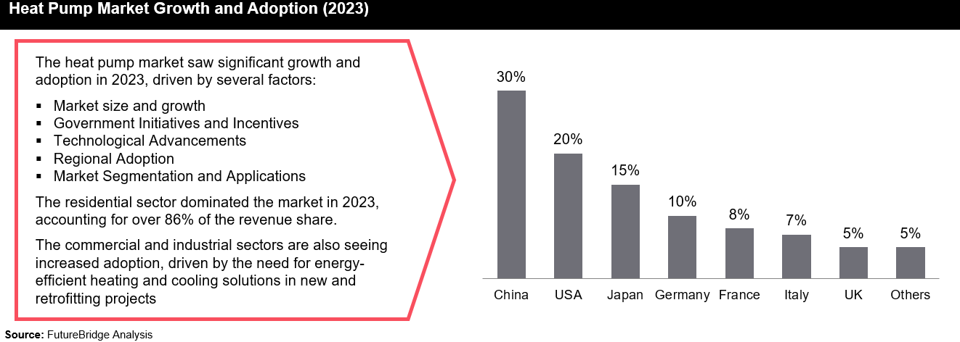

Regional Adoption Statistics:
- In Norway 60% of buildings are equipped with heat pumps.
- Sweden and Finland: Over 40% of buildings have heat pumps.
- China is leading the global market with the highest adoption and deployment of heat pumps.
- Europe: Significant growth from 1.2 million units in 2019 to 2.9 million units in 2023.
- North America has seen steady growth from 0.9 million units in 2019 to 1.7 million units in 2023.
- Asia saw the highest absolute number of heat pumps deployed, growing from 2.5 million units in 2019 to 4.3 million units in 2023.
Major Shift-Supportive government policies/incentives
Recent policy measures, such as fossil fuel heating bans, tax incentives, and heat pump mandates, have accelerated adoption, with notable growth in Italy, Germany, and Norway over the past five years.
- The U.S. Department of Energy’s initiatives, such as the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act and the Residential Cold Climate Heat Pump (CCHP) Technology Challenge, support innovation and deployment of next-generation heat pumps.
- Norway’s Enova Grants: Provides financial support for various energy efficiency measures, including heat pumps, covering a sizable portion of the installation cost.
- Sweden’s ROT Tax Deduction: Provides a 30% tax deduction on labor costs for installing heat pumps, up to a maximum of SEK 50,000 per year.
- Germany’s Market Incentive Program (MAP): Provides grants and subsidies for renewable energy systems, including heat pumps. Grants can cover up to 35% of the installation cost.
Market Trends and Growth of Heat Pumps by 2030
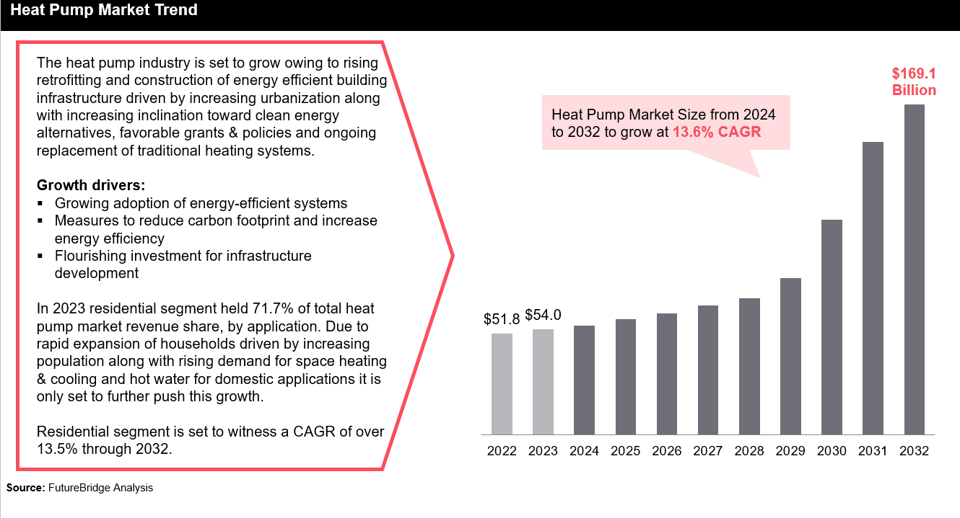
As the demand for efficient and sustainable heating solutions continues to grow, the heat pump market is expected to experience significant expansion. Rising demand for efficient heat and cooling solutions and shifting inclination toward energy efficiency is set to complement the industry landscape. Heat Pump Market was valued at USD 54 billion in 2023 and is set to attain about 13.6% CAGR between 2024 and 2032. Whereas for residential segment it is expected to increase at 13.5% between 2024-2032[7].

Benefits and future potential of advanced heat pumps
We recognize the transformative potential of heat pump technology in achieving sustainable and efficient heating solutions. Our focus on heat pumps is driven by their significant environmental benefits, cost savings, and alignment with global energy policies.
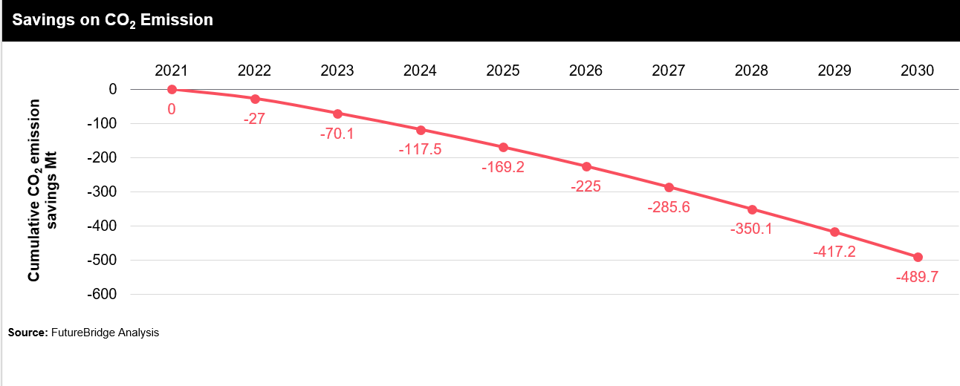
- Adopt Heat Pumps for Long-Term Savings: According to the U.S. Department of Energy, heat pumps can reduce electricity use for heating by approximately 50% compared to electric resistance heating such as furnaces and baseboard heaters. Additionally, the International Energy Agency (IEA) reports that heat pumps can cut global CO2 emissions by at least 500 million tons annually by 2030.
- Leverage Government Incentives: Many governments offer financial incentives for the installation of heat pumps. For example, the European Union’s Green Deal aims to install 10 million heat pumps by 2030, supported by various incentive schemes and regulatory measures. Also in the U.S., the federal tax credit for residential renewable energy products, including heat pumps, offers up to 26% of the installation cost, making it an attractive financial decision.
- Upgrade to Cold Climate Models: Because cold climate heat pumps are more efficient at low temperatures, they reduce the need for expensive backup heating systems, leading to significant savings on heating bills. Homeowners can save up to 50% on their heating costs by switching to cold climate heat pumps, as they use less electricity to generate the same amount of heat compared to electric resistance heating or older heat pump models.
- Integrating with Renewable Energy: Integrating heat pumps with renewable energy sources such as solar or wind power can maximize energy efficiency and sustainability, reducing reliance on fossil fuels. For example, A study by the University of Oxford found that combining heat pumps with solar photovoltaic systems can reduce household energy costs by up to 70% and significantly lower carbon emissions.
- Stay Informed on Technological Advances: The market for heat pumps is rapidly evolving with continuous advancements in technology. Staying updated on these innovations can help consumers make informed decisions and adopt the most efficient and effective systems
Foresight and Emerging Perspectives
The latest advancements in heat pump technology are reshaping the heating and cooling industry by delivering exceptional energy efficiency and advancing sustainability. This transformative shift is particularly evident in the global push towards reducing carbon emissions and achieving net-zero targets. By 2030, heat pumps are projected to contribute significantly to the global effort to reduce fossil fuel use. We at FutureBridge believe that the expansion of heat pump technology is not only a critical component of global climate strategies but also offers substantial economic benefits. By 2030, the heat pump market is projected to generate over $100 billion in revenue globally. Furthermore, the deployment of heat pumps is expected to create over 1 million jobs in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance sectors. The heat pump sector is experiencing robust growth, driven by key markets including China, the USA, and Japan where installations are expected to surge, supported by aggressive climate goals and substantial investments in renewable energy technologies.
FutureBridge believes, integration of advanced heat pump technologies along with robust policy measures, supportive frameworks, including tax incentives, rebates, and stringent regulations are crucial in this transition to phase out fossil fuel heating. With continued innovation and rising market adoption, heat pumps are poised to play a pivotal role in achieving net-zero emissions by 2050 and substantially reducing our reliance on fossil fuel-based heating and cooling systems.
Want to explore the best in heat pump technology and supportive policies? Our energy team is ready to help—contact us today!