Introduction
An individual needs to consume a meal containing a precise set of ingredients and appropriate nutritional values. 3D printing is a ground-breaking technology that can improve the nutritional value of meals and even address hunger issues in countries where fresh and affordable ingredients are inaccessible. The global food industry is adopting 3D printing technology to make food production more efficient and increasingly sustainable.
What is 3D printing?
3D printing is a technique used for the manufacture of three-dimensional objects with high accuracy and quality finishing in their dimensions. The technique finds applications in industries, including aviation, automotive, packaging, construction, pharmaceuticals, and food. In the food sector, 3D printing is widely investigated across areas, such as customized food designs, personalized and digitalized nutrition, simplified supply chain, and broadened source of available food material.
A 3D food printer comprises a food-grade syringe or cartridge that holds material, a real food item, and deposits exact fractional layers through a food-grade nozzle directly onto a plate or other surface in a layer-by-layer additive manner (refer Exhibit 1). Another method is a mold-based method wherein 3D printing food machines are used to give shapes to a dough with the help of a hollow container or molding box (refer Exhibit 2). 3D printing requires hardware and software to work in collaboration. Advanced 3D food printers are equipped with user-friendly interfaces and pre-loaded recipes with designs that can be easily accessed by the computer or even with a mobile or IoT device.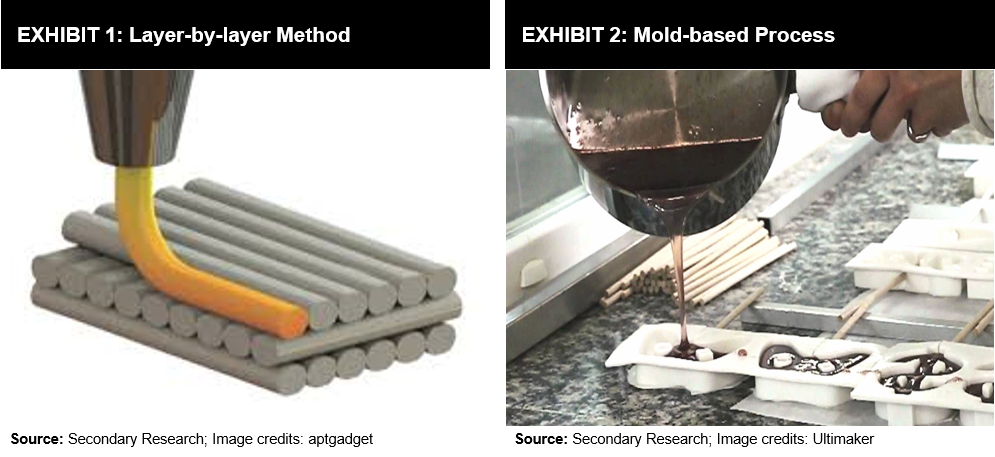
There are a variety of foods manufactured using 3D printers. A few of them are listed in Table 1: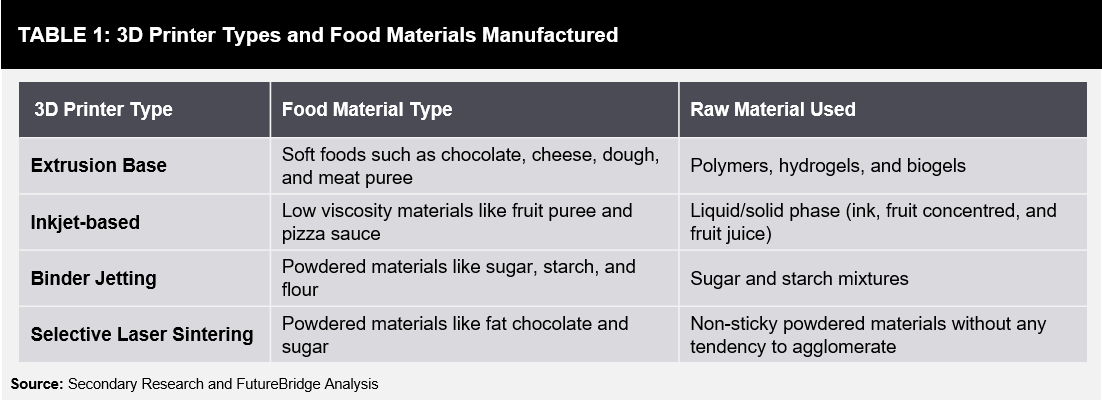
Currently, 3D food printers make use of nozzles, fine materials, lasers, and robotic arms. The raw material flows smoothly from the print cartridge to the printing platform and protects the solid build on the platform. In a similar fashion, substances such as starch and proteins, which can form hydrogel structures, can easily be obtained from cheese, chocolate, and humus that can easily flow from the printer cartridge to the platform.
The 3D printed food consuming community favors a variety of culinary options, such as crystallized sugar cake, detailed chocolate designs, ready-to-bake pizzas and ravioli, and cracker-like yeast structures having seeds and spores, which can sprout over time.
Benefits to look forward to…
3D printing usage comes with its own set of advantages:
- Allows food customization according to the choice, as the 3D printer can help determine the exact quantity of vitamins, carbohydrates, and fatty acids as per the input and assess the correct percentage of nutrients for a particular age.
- 3D printing saves both time and energy when it comes to experimenting with different types of food dishes. It also helps in achieving perfection with less effort and less time.
- The use of the food printing technique enforces innovation and creativity. Users can create dishes in entirely new ways by customizing ingredients. In addition, users of 3D printing can modify composition or amalgamate two products to produce an innovative dish.
- Food reproducibility is possible using 3D printing. Using the same set of ingredients to produce a similar dish again eventually drives the minimization of food waste. Additionally, it allows the sustainable usage of materials, such as duckweed, grass, insects, or algae, which can be used to form the basis of familiar dishes.
Challenging Aspects
A few challenges associated with the use of 3D printing are mentioned below.
Firstly, food safety is a significant concern. 3D printing process develops food in minimal time, which eventually restricts cooking food at certain temperatures or may result in fluctuating temperatures due to which microbes can grow and contaminate the food. Hence, to avoid contamination-related issues, manufacturers are required to follow certain standard practices and guidelines while processing the food.
Food manufacturers cannot use all ingredients that are used at the time of conventional cooking. Every ingredient has its storage and cooking requirements, such as an optimum temperature, which needs to be met. All ingredients cannot be placed together in one container, along with the main component or dough, when manufacturing food via 3D printing
The use of a 3D printing machine requires skillful personnel. Appropriate training is offered to individuals on how to use a 3D printer for food manufacturing, which results in high-cost investment. The knowledge base and skills needed to operate the machine adds to the cost for training purposes. Additionally, 3D printers are expensive, with prices ranging between USD 1,000 to USD 5,000. The use of skilled labor and machine cost exerts a huge burden on the manufacturer.
Market Scenario
The growth of 3D printing technology in the market depends on factors, such as the growing demand for 3D printed food products in the market and health perspective. Consumers, with the help of the internet, can check online databases for recipes to design their healthy diet by using the right ingredients in the meal. Before 2014, the food printing method was very complicated. However, at present, food manufacturing players are showing interest in 3D printing technology for food items manufacturing. These players are moving from conventional food preparation methods to advanced technologies, such as 3D printing.
Exhibit 3 represents a comparison between the top priorities related to 3D printing in 2015 and 2020, as reported in the Forbes Study.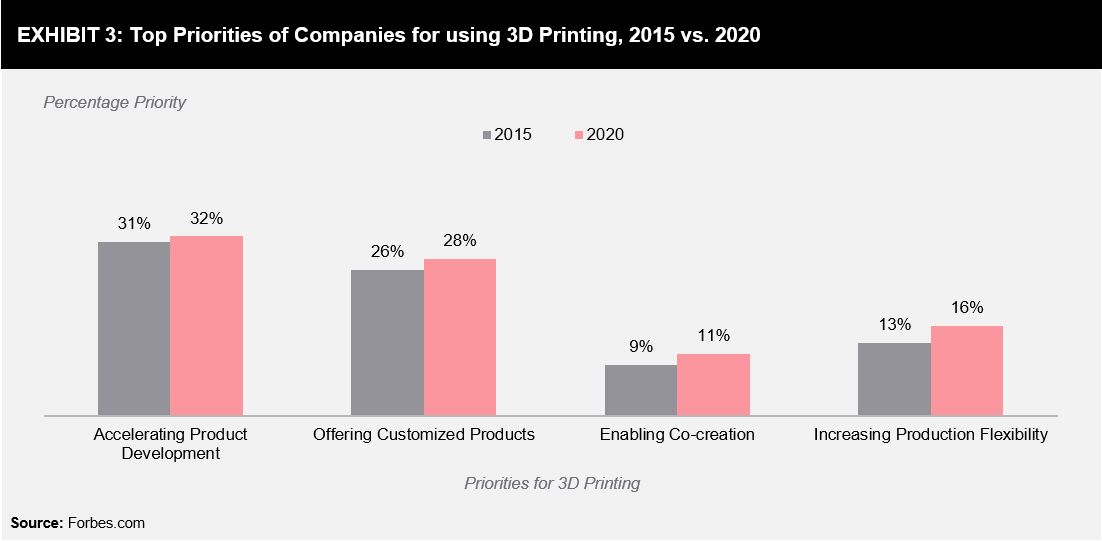
As per the survey, early adopters of 3D printing in Europe are more focused on offering customized products and increasing production flexibility, whereas their US-based counterparts are focused on factors of co-creation
Multiple companies are offering 3D printing machines, such as Natural Machines, 3D systems, XYZ printing, NuFood, byFlow, Bocusini, Mmuse, etc. Such companies supply 3D printing food machines to core food manufacturers of chocolates, cakes, pizzas, etc. A few examples of active players in the 3D printing market are mentioned in Table 2: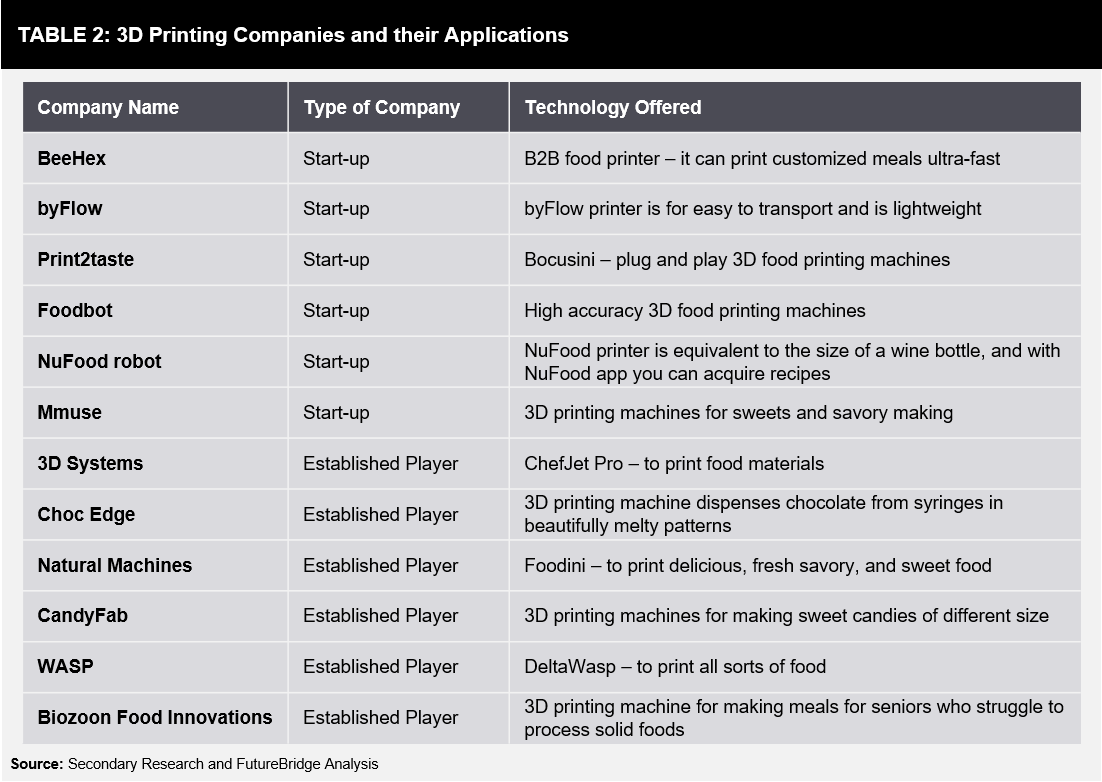
3D Printing Adoption Scenario
While there are companies still exploring the idea of technology potential, there are powerhouse brands, such as PepsiCo and Hershey, continuously using 3D printing. While PepsiCo uses 3D printing to create a plastic prototype of different shaped and colored potato chips, Hershey’s scientists use 3D printing for uniquely designed candy. Oreo has used 3D printing to create cookies with customized creme patterns and flavors. Barilla, an Italy-based pasta manufacturer, collaborated with TNO, a Dutch scientific research firm, to develop a 3D printer capable of printing a variety of differently shaped pasta, allowing customers to 3D print their CAD files with different pasta designs quickly and easily.
Recently, a Zurich-based leading manufacturer of high-quality chocolate and cocoa products, Barry Callebaut Group, announced the launch of the world’s first 3D printing studio to make personalized 3D printed chocolate at a large scale. It launched its chocolate creations through its global decoration brand, Mona Lisa. Mona Lisa teamed up with one of the most creative pastry chefs, Jordi Roca, to help him create ‘Flor de Cacao,’ a unique 3D piece made out of chocolate. It represents a cocoa bean that opens up like a cacao flower through contact with hot chocolate sauce.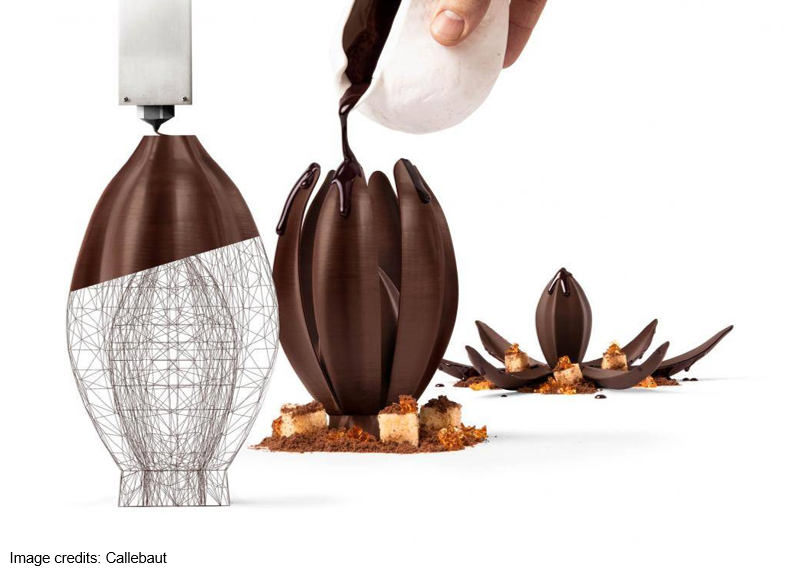
Conclusion
3D printing technology in food industries offers new possibilities, such as personalized nutrition, automated cooking, reduction in food wastage, etc. This 3D printing technology in the food industry can fulfill the unmet needs in terms of personalized nutrition, food wastage, demand, and availability of food. It is an evolving technology that has a large number of benefits, such as saving time, highly efficient, sustainability, and many more. Nowadays, food manufacturing companies are moving towards the techniques or methods that can help them use food ingredients in the right manner for making healthy and tasty food to reduce food wastages. The population of the world is increasing rapidly, so there will be an increase in the food demand as well as wastage of it will lead to food source scarcity. This situation needs to be handled with novel technologies, such as 3D printing, which can efficiently use food resources with no or very less amount of wastage.
Globally, there are a variety of prototype printers available for food production. 3D printing will continue to evolve as an exceptional technology in the food industry; however, high adoption will likely come from companies focused on product innovations and/or direct-to-consumer strategies.
References
- https://www.outsource2india.com/eso/mechanical/articles/3d-printing-impact-food-industry.asp
- https://www.3dnatives.com/en/fused-deposition-modeling100420174/
- https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/insights/focus/3d-opportunity/3d-printing-in-the-food-industry.html
- https://turbofuture.com/consumer-electronics/3D-Printers-For-Food-Technology-and-Applications
- https://www.forbes.com/sites/tjmccue/2018/10/30/3d-food-printing-may-provide-way-to-feed-the-world/#77c55a035817
- https://blog.grabcad.com/blog/2019/06/17/3d-printed-food-companies/
- https://www.aniwaa.com/food-3d-printers/
- https://www.disruptordaily.com/3d-printing-watch-food-industry/
- https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/d8e0/edd23846992b6eb8e1d25a51b752b4335879.pdf
- https://www.barry-callebaut.com/en/group/media/news-stories/barry-callebaut-opens-worlds-first-3d-printing-studio-craft-unseen
- https://www.forbes.com/sites/louiscolumbus/2019/05/27/the-state-of-3d-printing-2019/#27b44bc46c2c
Need a thought partner?
Share your focus area or question to engage with our Analysts through the Business Objectives service.
Submit My Business ObjectiveOur Clients
Our long-standing clients include some of the worlds leading brands and forward-thinking corporations.
- © 2021 Cheers Interactive (India) Private Limited. All rights reserved. FutureBridge ® is a registered trademark of Cheers Interactive (India) Private Limited.




































